Blue light
Blue light hazard is defined as the potential for a photochemical induced retinal injury resulting
from radiation exposure at wavelengths primarily between 400 nm and 500 nm. For the purposes of this discussion, blue light is defined as light within the wavelength range of 400-480 nm, because over 88% of the risk of photo-oxidative damage to the retina
from fluorescent lamps (cool white or ‘broad spectrum”) is due to light wavelengths in the
range of 400-480 nm. The blue light hazard peaks at 440 nm, and falls to 80% of peak at
460 and 415 nm. In contrast, green light of 500 nm is only one-tenth as hazardous to the retina than blue light with a wavelength of 440 nm. The mechanisms for photochemical induced
retinal injury are caused by the absorption of light by photoreceptors in the eye.
Under normal conditions when light hits a photoreceptor, the cell bleaches and becomes
useless until it has recovered through a metabolic process called the “visual cycle.
Absorption of blue light, however, has been shown to cause a reversal of the process
where cells become unbleached and responsive again to light before it is ready. This greatly
increases the potential for oxidative damage. By this mechanism, some biological tissues such as skin, the lens of the eye, and in particular the retina may show irreversible changes induced by prolonged exposure to moderate levels of UV radiation and short-wavelength light.
According to some of these studies, blue light waves may be especially toxic to those of us
who are prone to macular problems due to genetics, nutrition, environment, health habits,
and aging.
At present, LED to achieve white light, there are three main methods:
1, the LED of the three primary color chips red, green and blue multi-chip group and synthesis of white light.
Advantages:
- high efficiency,
- color temperature controllable,
- better CRI
Disadvantages: three primary colors decay caused by different color temperature instability. The control circuit is more complex and costly.
2, the yellow phosphor excited by blue LED chip and a phosphor emitted white light yellow-green synthesis
Advantages:
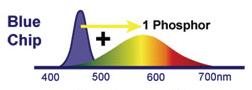
- high efficiency,
- simple preparation,
- temperature stability,
- good CRI
Disadvantages: poor consistency, color temperature variation with angle
3, excite phosphor emit ultraviolet LED chip synthesis tricolor white
Advantages: the CRI is good, simple preparation
Disadvantages: currently, LED chips efficiency is low, a UV light leakage, and the phosphor
temperature stability problems to be solved